The primary technology used for local networks is Ethernet. Other technologies exist, such as Token Ring and FDDI, but they are not recommended unless you are upgrading an existing network and you already have extensive experience with that other technology.

Wireless networking technologies take the concept of "no new wires" to the ultimate. In a wireless network, the computers in your home or office broadcast their information to one another using radio signals (see illustration at right). This can make networking extremely easy, especially if you have computers spread across your home or office. It also makes it a lot simpler to move computers around. For example, a laptop with a wireless network card is completely portable throughout the home or office!
Although there are a number of wireless technologies available, most everybody today uses the "Wi-Fi" standard (for "wireless fidelity", like Hi-Fi for "high fidelity" in audio equipment).
The advantages of Wi-Fi include:
Disadvantages include:
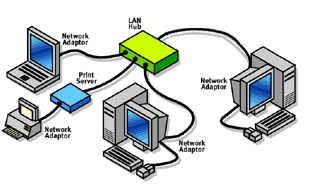
Wired networks use physical wires for the connections (see illustration at right) and faster speeds are possible than wireless networks.
Wired networks come in three "flavors": standard Ethernet, Phone-line networking and Power-line networking.
Ethernet is easily the most popular networking system available today. It is also one of the widest ranging systems. The equipment needed for an Ethernet-based network can be as simple as two network interface cards (NIC) and a cable, or as complex as multiple routers, bridges and hubs. It is this versatility that makes it so attractive to homes and businesses.
Ethernet has many advantages:
And a few disadvantages:
Phone-line networking, commonly referred to as "HomePNA", uses your existing phone lines to connect the local network. HomePNA is based on the specifications developed by the Home Phone Networking Alliance (HPNA). The HPNA is a consortium of key networking technology companies that created a phone-line standard for the networking industry.
HomePNA has several advantages:
HomePNA does have some drawbacks, though:
Like HomePNA, power-line networking is based on the concept of "no new wires." The convenience is even more obvious in this case because while not every room has a phone jack, you will always have an electrical outlet near a computer. In power-line networking, you connect your computers to one another through the same outlet. Because it requires no new wiring, and the network adds no cost to your electric bill, power-line networking is the cheapest method of connecting computers in different rooms.
Advantages of a Power-line network include:
Power-line networking also has some drawbacks:

A "hybrid" network uses two or more technologies within the same network. Normally it's a network that supports both wired and wireless connections. For example, a network might consist mostly of wired connections, but also allow laptops with a wireless interface card to connect (see illustration at right).